

No controllers online
Controller Schedule
February 24th, 2026
No sessions found for selected date
As a controller, one of the easiest things you can do to improve your life and that of your fellow controllers is to work on timely handoffs. Nearly every controller will find him or herself guilty of holding onto an aircraft too long. The result can range from delays at the runway to airspace busts or go-arounds, but it is almost always bad for everyone involved.
So, when should you hand an aircraft off to the next controller? As soon as you no longer need to talk to the aircraft. It really is as simple as that. If there is nothing more you anticipate needing to say to a pilot, hand them off to the next controller or approve a frequency change if there’s not a “next” controller.
Let us look at a couple of practical examples, starting with LA Ground.
As a ground controller, your primary mission is the safe and efficient movement of aircraft around the airport. For our purposes, that means not crashing airplanes into one another, and getting them to the correct location on the airport. The biggest opportunity you will have to elevate your handoffs while working LA Ground is when aircraft are taxiing from Terminals 4 through 8 to Runway 25R.
First and foremost, make sure the pilot is on the correct taxiway and headed in the correct direction (the green arrow in the diagram below). Pilots may be unfamiliar with the field or get disoriented, so it is important to make sure they’re going where you want them to go and that they won’t get lost.
Secondly, you want to make sure that there are no conflicts with other aircraft, which would most likely take the form of an aircraft coming out of the “Box” or one of the cargo/GA pads north of the 25R departure end (the orange boxes). Absent any potential conflicts from those areas, there is no reason you shouldn’t advise the pilot to contact Tower (or the controller staffing that position) as the aircraft approaches C5 (the yellow circle) or, at the latest, C3 (the red circle).
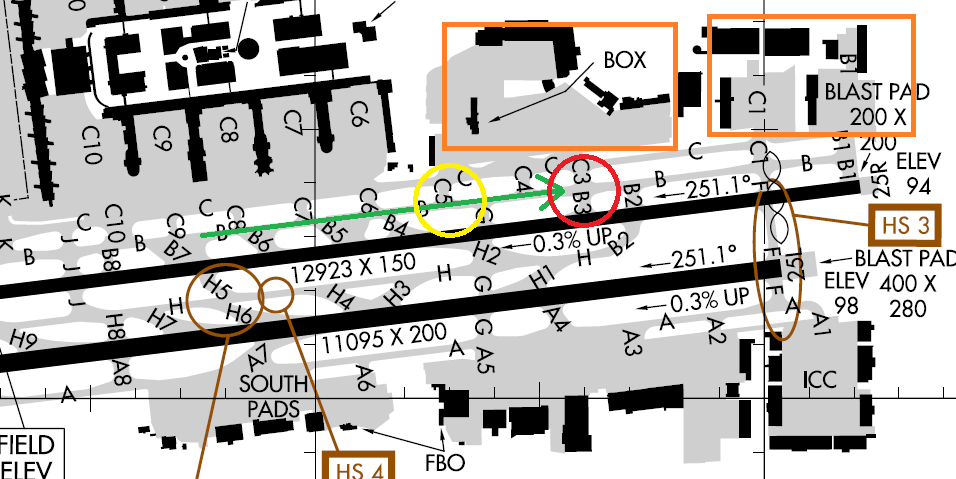
There are numerous operational advantages for all parties involved. As the Ground controller, you relieve yourself of the burden of remembering to hand off the aircraft later. Anyone who has received an annoyed transmission from a pilot or message from a Tower controller can relate to this. Additionally, pilots may switch to Tower on their own. This is quite common in the real world but can result in confusion when on VATSIM.
From the pilot’s perspective, an early handoff makes better use of their time. It is also important to remember that a handoff isn’t instantaneous. The pilot’s workload may not allow for them to switch over immediately, so build in time for that to happen.
Additionally, by giving the Tower controller (or the radar controller providing Tower services) more time with the aircraft, you open up a wealth of options: intersection departures, takeoff clearances without the aircraft coming to a stop, and more.
Now let us look at a radar example but stay in the area of KLAX.
Working a departure position (be it sectorized or as part of a larger area of responsibility) is an excellent example of both needing a timely handoff from Tower (remember Tower controllers: as soon as you see the altitude block increment, ship ‘em to Departure!) and wanting to ensure a timely handoff to Center. Let’s look at everyone’s favorite example, the ORCKA 5 departure out of KLAX.
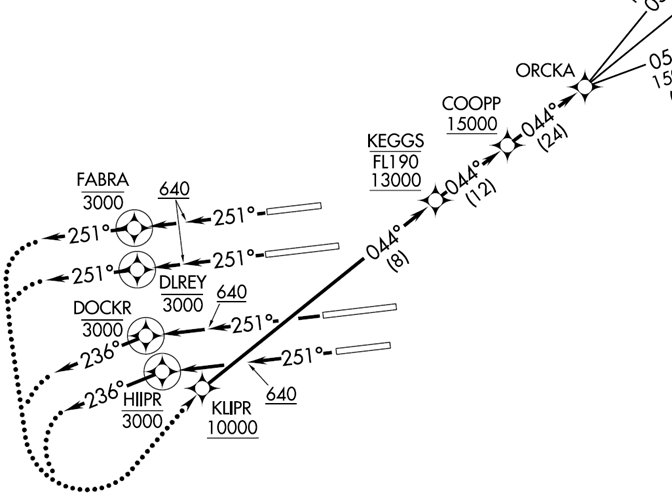
As the Departure controller, you’re going to still be focused on the same two tasks as earlier: the safe and efficient movement of the aircraft. In this instance, we of course want to prevent loss of separation – that’s our top priority. Secondly, we want to make sure the traffic departs the terminal area efficiently and gets headed toward its ultimate destination. No one on the ORKCA5 is looking to fly heading 251 or 236 a minute longer than they must.
After establishing radar contact with the departing aircraft, your first instruction will likely involve canceling the restriction that they stop their climb at 5,000 feet. This is accomplished either through “climb and maintain one-three thousand” or “climb via the ORCKA Five departure” if you still need compliance with the published crossing restrictions.
The next instruction (provided you didn’t have to correct an erroneous pilot) will likely be the left turn back toward KLIPR. This instruction is usually provided as the aircraft is climbing through 5,000 feet, which serves two purposes. One, by observing the climb through 5,000 feet, you’ve verified the aircraft has correctly canceled the restriction they received on the ground to level off at 5,000. Secondly, at that point they are over halfway to their vertical goal of crossing KLIPR at or above 10,000 feet and can start the turn.
Looking ahead on the SID, you’ll notice things progress quickly and if left unmonitored, an aircraft climbing via the SID can climb out of your airspace in little time. So, let us review our checklist:
If these criteria are met, it’s time to initiate the handoff to the next controller. Even though your airspace goes all the way up to 13,000 feet, you gain nothing by holding onto the aircraft. And you run the very real risk of forgetting about the aircraft and a) having it level off at 13,000, or b) having it bust through your airspace if it’s climbing via the SID (note: the ORCKA5 has a top altitude of FL230).
Adding to the delay in the handoff from a pilot’s perspective of changing frequencies, you also now need to consider the delay in the next controller seeing your handoff. By building in this extra time, you give everyone more breathing room while also freeing up your resources for the next pilot who just took off. And you never know, that next one could be someone trying a right-turn off the deck toward KLIPR – you’ll be glad you made things easier on yourself.
Ultimately, there is no reason to hold onto an aircraft until they are right at the end of your airspace or jurisdiction. You do not increase your level of interaction with the traffic, and you do not increase safety or efficiency. All you risk doing is causing undue delays or worse, a loss of separation. Keep in mind, this is a lesson that applies at every controller position, from Ground to Center, and most controllers would benefit from being more proactive with their handoffs.