Los Angeles ARTCC VFR Operations
Introduction and Purpose
This document is standard operating procedure for VFR operations throughout ZLA. Refer to VFR Clearances section of the STM for more information on VFR departures.
Facility SOPs may conflict. In the event of a conflict, follow the facility SOP.
VFR Radar Services
Radar services are always provided for aircraft operating within Class C and Class B airspace. (7110.65 7-8-2, 7-9-2.)
Radar services for aircraft outside of Class C or Class B airspace are provided on a workload-permitting basis. (7110.65 7-8-2, 7-9-2.)
The pilot may request radar service termination once outside of Class C or Class B airspace. ATC may terminate radar service if workload precludes providing radar services outside of Class C or B airspace.
Radar services for aircraft operating within a TRSA are optional for pilots. When requested, provide TRSA radar service per 7110.65 7-7. ATC may terminate radar service once the aircraft leaves the TRSA (7110.65 7-7-7).
Flight Plans
Real-world VFR flight plans in the United States are not transmitted to air traffic control. They are sent to flight service stations for search and rescue purposes. VATSIM does allow pilots to file VFR fight plans; however, only filed remarks are retained in CRC.
Therefore, when aircraft are to receive flight following, ATC must ask the pilot for the aircraft type and any other information required by this SOP.
Aircraft not receiving flight following should not have a flight plan completed.
If a pilot departing a Class C or Class B airport declines flight following on the ground, note "negative radar service" in the flight plan remarks. The pilot must still receive instructions as noted in this SOP. The radar controller will terminate radar service once the aircraft is outside of Class C or Class B airspace.
Class D Airports
- Flight Following: Aircraft departing Class D airports receive following only on pilot request. If flight following is requested by the pilot, use Class C procedures.
- Flight Plan: No flight plan.
- Clearance: There are no VFR instructions or clearances given by ground control. Pilots should call ground control stating direction of flight and ready to taxi with the current ATIS information.
Class C Airports
- Flight Following: Aircraft departing Class C airports receive flight following by default. It is required for all VFR departures while inside Class C airspace.
- Flight Plan:
- Aircraft type
- Departure and arrival airports (The arrival airport is not necessary if the pilot will cancel once leaving the airspace.)
- VFR cruise altitude
- Discrete beacon code (squawk)
- Clearance: Provide departure frequency and squawk. Include initial heading and/or altitude as required by SOP.
- Notes: If the pilot does not want flight following, add "negative radar service" in the remarks. This will inform the radar controller to terminate radar service once the aircraft is outside of Class C airspace.
Class B Airports
- Flight Following: Aircraft departing Class B airports receive flight following by default. It is required for all VFR departures while in Class B airspace.
- Flight Plan:
- Aircraft type
- Departure and arrival airports (The arrival airport is not necessary if the pilot will cancel once leaving the airspace.)
- VFR cruise altitude
- Discrete beacon code (squawk)
- Clearance: Provide bravo clearance, departure frequency and squawk. Include initial heading and/or altitude as required by SOP.
- Notes: If the pilot does not want flight following, add "negative radar service" in the remarks. This will inform the radar controller to terminate radar service once the aircraft is outside of Class B airspace.
Class D Airports within a TRSA (PSP)
- Flight Following: Optional - All VFR departures from PSP receive flight following unless the pilot declines (7110.65 7-7-7).
- For all VFR aircraft departing PSP, use Class C procedures.
- If the pilot declines, use Class D procedures.
Closed Traffic at Class C or D Airports
- Pilots should call requesting closed traffic and ready to taxi. No clearance is provided, only taxi instructions. No FP is used or filed. Pilots shall squawk VFR (1200) in the pattern by default.
Closed Traffic at Class B Airports
- Aircraft should be cleared to enter bravo airspace and assigned a squawk. After readback is correct, they should call when ready to taxi.
- Example: "Cleared to enter San Diego Bravo airspace. Squawk 1234."
- The flight plan for Class B closed traffic should only have aircraft type, a voice tag, and "VFR" in the altitude field. Avoid adding extra information.
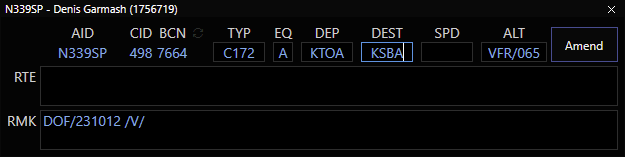
Example VFR Flight Plan for Flight Following
VFR Practice Approaches
- Class B, Class C, and TRSA Procedures:
- Standard VFR separation services are provided.
- Clear VFR aircraft using appropriate approach clearance phraseology except replace altitude assignment with "MAINTAIN VFR."
- SCT and L30 TRACONs shall use these procedures.
- Class D, E, and G Procedures:
- No separation services are provided.
- PHRASEOLOGY: "(Aircraft identification) MAINTAIN VFR, PRACTICE APPROACH APPROVED, NO SEPARATION SERVICES PROVIDED."
- Missed approaches are not automatically authorized for VFR aircraft. (7110.65 4-8-11)
- Prior to approach clearance or approval, the radar controller should ask the pilot to advise intentions. Example: "N123SP, how will this approach terminate?"


